VAD in VoIP: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How It Saves You Money
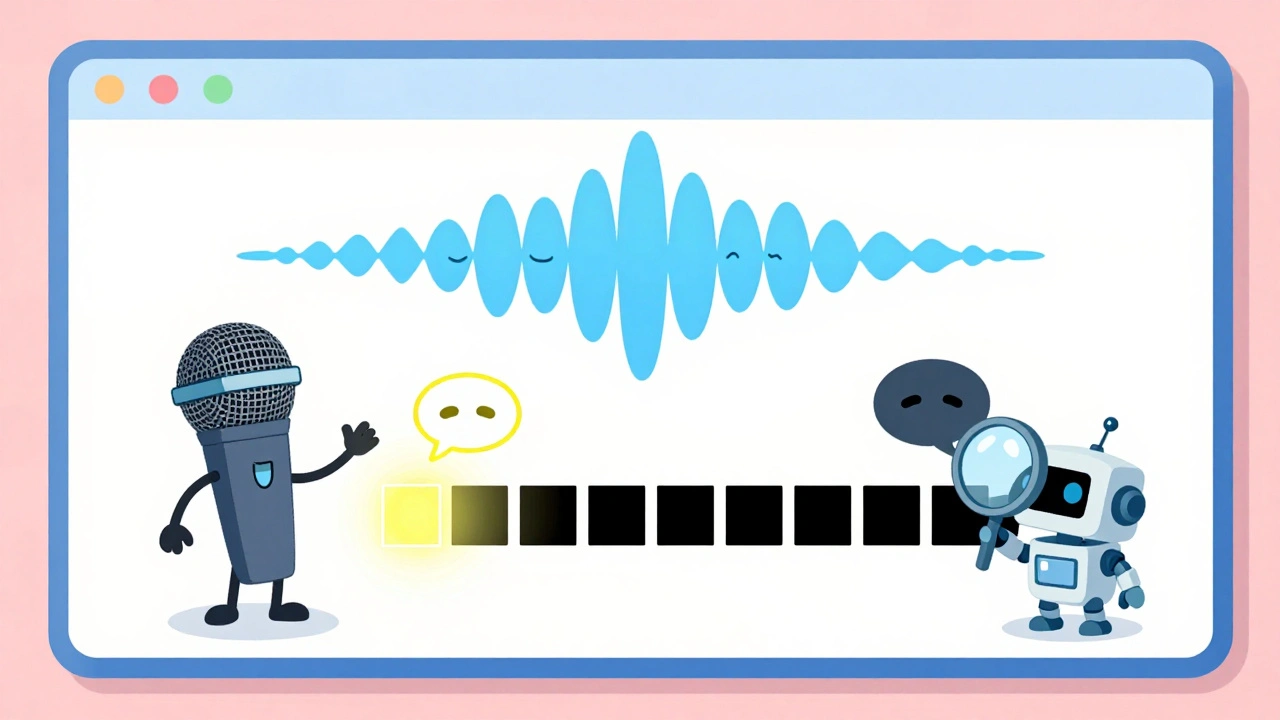
When you're on a VoIP call, your device doesn't send audio nonstop—it only transmits when you're talking. That's thanks to VAD, Voice Activity Detection, a technique that identifies speech in real time to reduce unnecessary data transmission. Also known as silence suppression, it's a quiet but powerful part of how modern VoIP keeps calls clear and cheap. Without VAD, every second of your call—whether you're talking, pausing, or just breathing—would use up bandwidth. That's a waste. With it, your system learns the difference between speech and silence and only sends data when it matters.
VAD works hand-in-hand with codec negotiation, the process where your phone and the other end agree on which audio format to use, like G.711 or Opus. If VAD says you're silent, the codec stops encoding. That cuts bandwidth by up to 50% during typical conversations. For businesses with hundreds of daily calls, that means lower internet bills and less strain on the network. But VAD isn't perfect. Sometimes it misreads a long pause as silence and cuts off the start of your next sentence. Or worse, it thinks background noise—like a dog barking or a fan running—is speech and keeps transmitting. That’s why top VoIP systems let you tweak VAD sensitivity, and why providers like Five9 and Talkdesk test it under real office conditions.
It’s not just about saving money. VAD also helps with call blending, the way call centers manage inbound and outbound calls by sharing agent resources. If agents are handling both types of calls, VAD ensures their idle time doesn’t flood the network with useless data. That keeps the system responsive. And in cloud VoIP setups where multiple companies share the same infrastructure, VAD helps isolate traffic, making shared tenant isolation, the security method that keeps your calls private from other businesses on the same server more effective. Less noise means fewer conflicts and better call quality for everyone.
You’ll find VAD in almost every modern VoIP system—from cordless SIP phones to AI-powered call centers. But not all implementations are equal. Some cheap hardware turns it off to cut costs. Others over-aggressively suppress silence, making calls feel robotic. The best systems use adaptive VAD that learns your voice patterns and adjusts in real time. If you’re setting up a new VoIP system, check the specs: does it support VAD? Can you adjust its sensitivity? Is it enabled by default? These aren’t just technical details—they’re your first line of defense against bloated bills and dropped conversations.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on how VAD interacts with codecs, call centers, and cloud infrastructure. No fluff. Just how it works, what to watch for, and how to make sure your system gets it right.